What is a Condensation Reaction?
In Acid Catalysed Aldol Condensation, Condensation is an addition reaction wherein two or more molecules join to produce a single molecule, eliminating minor molecules such as water, hydrogen sulphide, ethanol, ammonia, and acetic acid.
A dehydration reaction occurs if a water molecule is removed. Condensation reactions include the Aldol reaction, the Knoevenagel reaction, the Claisen reaction, and the Dieckman reaction.
Introduction of Aldol Condensation
Aldol is an acronym for alcohol and aldehyde. It is a condensation reaction in which aldehyde or ketone dimerization occurs. In this reaction, an enolate ion combines with a carbonyl chemical to produce a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, followed by the elimination of a water molecule to produce a conjugated enone.
- Alpha hydrogen must be present in the carbonyl molecule for aldol condensation to occur.
- Aldol condensation is the condensation that happens between identical carbonyl molecules.
- Crossed aldol condensation is the condensation of two distinct carbonyl molecules.
CH3-CHO + CH3-CHO → CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CHO
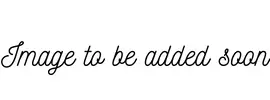
Acid Catalysed Aldol Condensation
Acid catalysed Aldol Condensation is an aldol condensation reaction taking place in the presence of an acid. It involves a particular of aldehyde or ketone. A conjugated enone is produced when an enol interacts with a carbonyl chemical to make a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, accompanied by the removal of water molecules.
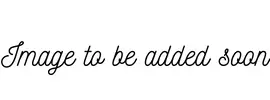
Mechanism of Acid Catalysed Aldol Condensation
Step 1: Activation of Carbonyl Centre
In the initial step, the lone oxygen pairs attract the proton released by the acid, thereby protonating the carbonyl oxygen.
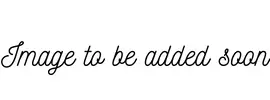
Step 2: Enolisation
In the second step, intermediate 1 interacts with the conjugate base of the acid to generate the nucleophilic enol.
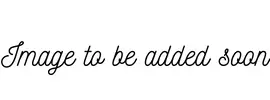
Step 3: Nucleophilic Addition
In the third step, the enol produced in step two serves as a nucleophile that attacks the activated carbonyl molecule to produce an aldol addition product.
Step 4: Dehydration
In the fourth phase, water is eliminated spontaneously, resulting in a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone.
Base Catalysed Aldol Condensation
Base Catalysed Aldol Condensation is an aldol condensation reaction taking place in the presence of a base. It involves the dimerisation of aldehyde or ketone. An enolate ion combines with a carbonyl chemical to produce a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, with the removal of water molecules to produce a conjugated enone.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs on Acid Catalysed Aldol Condensation
Q.1 What is a condensation reaction?
Condensation is an addition reaction in which many molecules join to produce a single molecule, eliminating tiny molecules such as water, hydrogen sulphide, ethanol, ammonia, and acetic acid. A dehydration reaction occurs if a water molecule is removed.
Q.2 What is aldol reaction?
Aldol is an acronym for alcohol and aldehyde. It is a condensation reaction in which aldehyde or ketone dimerization occurs. In this reaction, an enolate ion combines with a carbonyl chemical to produce a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, followed by the elimination of a water molecule to produce a conjugated enone.
Q.3 What is acid catalysed aldol condensation?
Acid catalysed aldol condensation is a condensation of aldol that occurs in the presence of an acid. It involves the dimerisation of aldehyde or ketone. A conjugated enone is produced when an enol interacts with a carbonyl chemical to make a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, accompanied by the removal of water molecules.
Q.4 What is base catalysed aldol condensation?
Aldol condensation in the presence of a base is referred to as base-catalyzed aldol condensation. It involves the dimerisation of aldehyde or ketone. An enolate ion combines with a carbonyl chemical to produce a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone, with the removal of water molecules to produce a conjugated enone.
Q.5 What is crossed aldol condensation reaction?
Crossed aldol condensation is an alternative to aldol condensation. It involves the condensation of two distinct carbonyl molecules.

