What is an Acid Anhydride?
An acid anhydride is a type of molecule that is able to produce an acidic solution when it is dissolved in water. Before delving further into it. Let’s recall some fundamental ideas.
Acids are compounds that are willing to transfer hydrogen ions to water.
Bases are chemicals that produce hydroxide ions in water.
What is Anhydride?
Anhydride means “without water.” It is the chemical substance that results after removing water from another compound. With water, anhydride produces either a base or an acid.
Acid Anhydrides – Definition & Meaning
An acid anhydride is a non-metallic oxide that, when reacted with water, produces an acidic solution. Organic acid anhydrides include the functional group R(CO)O(CO)R’ in organic chemistry. When one equivalent of water is removed from two equivalents of an organic acid in a dehydration reaction, organic acid anhydrides frequently occur.
In inorganic chemistry, an acid anhydride is an acidic oxide that interacts with water to generate an oxyacid (oxygen-containing or carbonic acid-containing inorganic acid) or with a base to form a salt.
Let’s try to gain a better understanding of the following reaction.
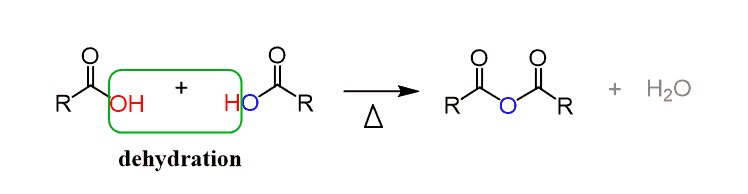
Synthesis of Acid Anhydride
Two carboxylic acids are heated at a high temperature of about 800°C in order to produce an organic acid anhydride. This mechanism removes one water molecule from the reaction. It can be produced by combining carboxylic acid with P2O5.
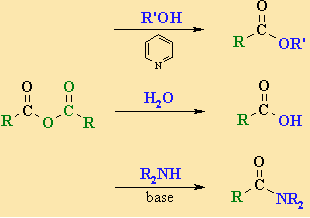
Chemical properties of acid
The -OCOR group of acid anhydride undergoes a nucleophilic substitution process. It is less reactive than acid chlorides due to the more electronegative nature of the Cl atom relative to the -OCOR group.
Formation of Sulphuric acid:
When sulfur trioxide combines with water, sulphuric acid is produced. As such, it can be chemically described.
SO3(g) + H2O → H2SO4(aq)
Sulfur trioxide gas eventually reacts with water to produce sulphuric acid. Airborne sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen to produce sulfur trioxide. When it combines with water during rain, acid rain is produced. These are extremely detrimental to the ecosystem.
Uses of Acids Anhydrides
There are various uses for acid anhydrides in organic chemistry.
- They are used in the production of several items, including medications, industrial chemicals, explosives, and fragrances.
- acetylation of alcohols for ester synthesis
- Construction of Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin)
- Deacetylation of morphine leads to the formation of heroin.
- Use as a protective group
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1 Why are acid anhydrides so reactive?
Because the electron donation to one carbonyl group competes with the electron donation to the second carbonyl group, anhydrides are less stable. Therefore, anhydrides are more reactive than esters, where only one carbonyl group must balance the oxygen atom.
Q.2 What is acid anhydride and examples?
Typically, anhydrides of inorganic acids are oxides of nonmetal substances. The anhydride of carbonic acid, H2CO3, is carbon dioxide, CO2. Nitric acid is the anhydride of nitrogen pentoxide, N2O5. The pentoxide of phosphorus, P2O5, is the anhydride of phosphoric acid, H3PO4.
Q.3 What is the formula of acid anhydride?
Two acyl groups are present in acid anhydrides, which have the general formula RC(=O)OC(=O)R, or acyl—O—acyl. The acyl groups might be identical (symmetric) or dissimilar (asymmetric or mixed). The simplest and most prevalent acid anhydrides are symmetrical monobasic acid derivatives.
Q.4 What is anhydride used for?
In organic synthesis, organic anhydrides are utilized to introduce the acyl group (RCO). With water, they produce carboxylic acids, alcohols and phenols, esters, and with ammonia and amines, amides.

