What is the full form of MAC?
The MAC full form is the Media Access Control Address. The MAC address is the hardware identification number. Specifically, each computer’s NIC (network interface card), such as a Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or Ethernet card, has a MAC address that was set by the manufacturer at the time of production and remains unchanging. Nortel, Dell, Nortel, and Cisco are among the well-known NIC manufacturing businesses. By replacing the NIC cards, it is possible to adjust the system’s default address.
Read Other Full Forms
Concise history of MAC
- As far as history is concerned, humans can believe that MAC addresses were created by Xerox PARC researchers.
- A network device’s MAC address is comprised of numerous related concepts, including physical address, hardware address, and Ethernet hardware address.
- Even BIA (burned-in address, especially for Cisco Router Switches) typically refers to the same thing.
Aspects of MAC
- The NIC is a computer circuit card that enables users to connect their computer to a network. It converts the data into an electrical signal that can be delivered through the internet.
- Therefore, a system’s hardware address includes an IP address.
- MAC addresses are matched with network adapter hardware, whereas IP addresses are associated with TCP/IP.
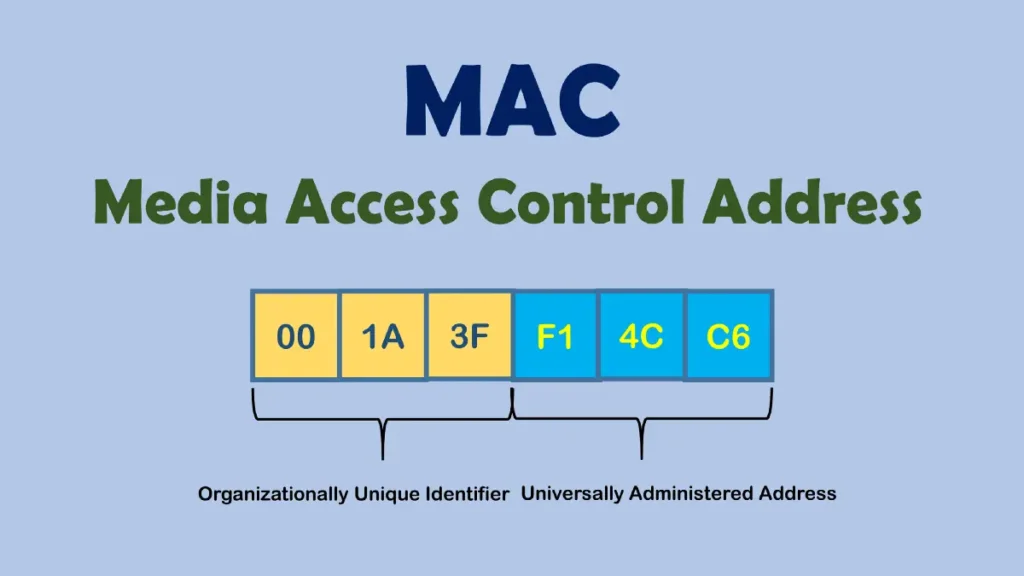
- The first six digits of the MAC address provide manufacturer information and are known as the OUI (Organizational Unique Identifier).
- The final six numbers are used to identify a Network Interface control system assigned by the manufacturer.
- The network instantly recognizes the number, therefore we do not need to remember the address.
- The IEEE Registration Authority Committee assigns their licensed suppliers’ MAC prefixes.
Advantages of MAC
- There are no or no attachment fees associated with network-connected systems.
- They have established a policy for the switch. Whether it has mounted permitted equipment or non-authorized equipment, regardless of who is tied to it.
- The MAC addresses are unique for each user inside the same subnet.
- The efficiency of MAC addresses simplifies the diagnosis of network issues connected to IP addresses, etc.
- Using the MAC address, a network administrator recognizes the sending and receiving of data on the network consistently.
- The only explanation for this is that, unlike dynamic IP addresses, MAC addresses do not change over time.
The limitations of the MAC
- Due to the fact that the first three bytes (OUI) of a MAC address are reserved for the manufacturer, only 224 unique addresses per OUI may be used by the same manufacturer.
- For MAC address sorting, we may assert that spoofing is simple. Due to the broadcast nature of Ethernet, it is possible to operate anonymously and only listen to and from authorized MAC addresses.
- An attacker can typically get network access by repeatedly changing his MAC address to one that is permitted.

