What is the full form of pH?
The pH full form is the “Potential of Hydrogen.” pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the concentration of H+ ions. Consequently, the name pH refers to the hydrogen’s strength or force. pH denotes the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, which indicates its acidity or basicity. On a pH scale, pH values range from 0 to 14.
Read Other Full Forms
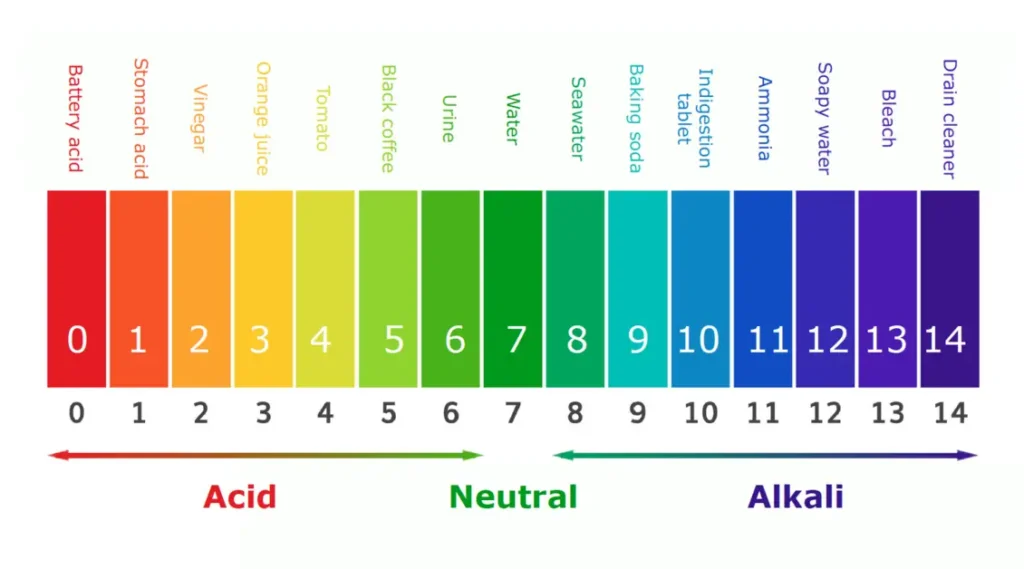
What are the pH Values for Acid and Base?
The pH range of the solution is 0 to 14.
- On the pH scale, solutions with a pH value between 0 and 7 are referred to be acidic solutions.
- Solutions with a pH value between >7 and 14 are referred to as basic solutions.
- On a pH scale, solutions with a potential of hydrogen or a pH value equal to 7 are known as neutral solutions.
Those solutions having a pH value of 0 are regarded as severely acidic. In addition, the acidity reduces as the pH value rises from 0 to 7, although solutions with a pH value of 14 are considered to be extremely basic. The acid and base strengths are proportional to the number of H+ and OH– ions formed. Acids with a greater concentration of H+ ions are known to be strong acids, and vice versa.
Significance of pH
- A living creature can only tolerate a limited range of pH fluctuations, and any more pH variations will make survival harder. In the event of acid rain, for instance, the pH of the water is less than 7. As it flows into a river, it decreases the pH of the water, which is detrimental to the survival of marine life.
- The lining of the human stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which aids in digestion by activating specific enzymes. In cases of acid reflux, antacids are used to neutralize the acid produced in the stomach.
- Frequently, the bacteria in our mouths reduce the pH of our mouths by creating acids through the breakdown of food particles. This leads to tooth demineralization and tooth decay. Since mouthwash neutralizes acid and aids in remineralization, it is recommended that we clean our teeth and mouths. Fluoride toothpaste promotes remineralization and protects against tooth decay.
- In the instance of a bee sting, the injection of formic acid (methanoic acid) through the sting causes severe pain. As a result, it is commonly advised to apply baking soda or other mild bases to the surface to neutralize the acid and preserve the pH.

