MLC Full Form: Everything You Need to Know
Are you puzzled by the acronym MLC and wondering what it stands for? In this article, we’ll explore the MLC full form, its definition, uses, and more. Whether you’re a student, professional, or just curious, you’ll find everything you need to know about MLC in the Below Article.
Read Other Full Forms
What is MLC?
MLC stands for Multi-Level Cell. It is a type of NAND flash memory that can store multiple bits of data per cell. In simple terms, MLC is a technology that allows more data to be stored in less space. It is used in various electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, USB drives, and solid-state drives (SSDs).
MLC Meaning in Different Contexts
MLC has different meanings in different contexts. Here are some of them:
- Medical-Legal Consultant: MLC is also known as a medical-legal consultant. It is a professional who assists lawyers, insurance companies, and other organizations in dealing with medical issues related to legal cases.
- Machine Learning Compiler: In the field of computer science, MLC stands for Machine Learning Compiler. It is a program that converts machine learning models into executable code.
- Marine Life Conservation: MLC can also refer to Marine Life Conservation, which is the protection and preservation of marine ecosystems and species.
Types of MLC
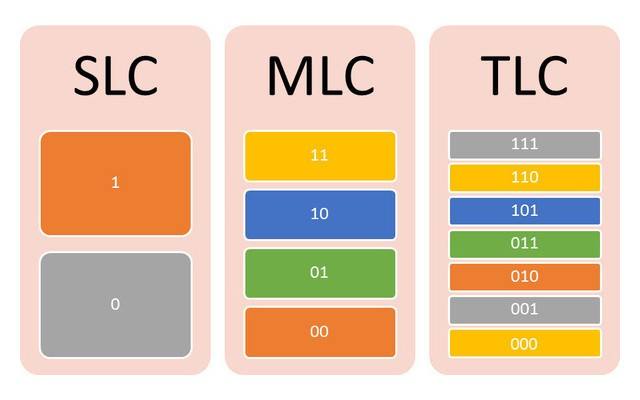
There are two types of MLC: 2-bit MLC and 3-bit MLC. 2-bit MLC can store two bits of data per cell, while 3-bit MLC can store three bits of data per cell. The latter is also known as Triple-Level Cell (TLC).
How Does MLC Work?
MLC works by using multiple voltage levels to represent different states of the cell. In 2-bit MLC, there are four possible voltage levels, each representing two bits of data. In 3-bit MLC, there are eight possible voltage levels, each representing three bits of data. The more voltage levels a cell can store, the more bits of data it can hold.
MLC vs. SLC vs. TLC
SLC stands for Single-Level Cell, and it can store only one bit of data per cell. On the other hand, TLC (Triple-Level Cell) can store three bits of data per cell. SLC is the fastest and most durable of the three, but it is also the most expensive. MLC strikes a balance between speed, durability, and cost, making it the most popular choice for most applications.
Applications of MLC
MLC is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Consumer electronics: MLC is used in smartphones, laptops, tablets, and USB drives to store data.
- Solid-state drives (SSDs): MLC-based SSDs are faster and more reliable than traditional hard disk drives.
- Cloud computing: MLC-based SSDs are used in cloud servers to provide faster and more efficient storage.
- Industrial and automotive: MLC is used in industrial and automotive applications that require high endurance and reliability.
Pros and Cons of MLC
Pros:
- More cost-effective than SLC
- More durable than TLC
- Faster read and write speeds than TLC
Cons:
- Less durable than SLC
- Slower read and write speeds than SLC
MLC and Data Storage
MLC has revolutionized data storage by enabling the creation of high-capacity storage devices in smaller form factors. It has also reduced the cost of data storage, making it more affordable for consumers and businesses. MLC-based solid-state drives (SSDs) have become increasingly popular due to their fast read and write speeds, low power consumption, and durability.
MLC and SSDs
MLC is widely used in SSDs due to its cost-effectiveness and performance benefits. MLC-based SSDs are faster and more reliable than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and offer faster boot times, improved system responsiveness, and faster data transfer rates. However, MLC-based SSDs are less durable than SLC-based SSDs and may wear out faster over time.
MLC and NAND Flash Memory
MLC is a type of NAND flash memory, a non-volatile memory technology that does not require power to retain stored data. NAND flash memory is used in a wide range of electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, and USB drives. MLC-based NAND flash memory offers higher storage capacity than SLC-based NAND flash memory and is more cost-effective than SLC.
MLC and Cloud Computing
MLC-based SSDs are widely used in cloud computing to improve storage efficiency and performance. Cloud servers require fast, reliable storage solutions to provide seamless access to data and applications. MLC-based SSDs offer faster read and write speeds, higher storage density, and lower power consumption than traditional hard disk drives, making them an ideal choice for cloud computing applications.
Future of MLC
MLC technology is constantly evolving, and future advancements are expected to further improve its performance and durability. As the demand for high-capacity, high-performance storage solutions continues to grow, MLC-based SSDs are likely to become even more popular in the future. However, new technologies like 3D NAND flash memory and QLC (Quad-Level Cell) may also pose a challenge to MLC in the coming years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MLC is a critical technology that has revolutionized the storage industry by enabling the creation of high-capacity, high-performance storage devices. Its cost-effectiveness, performance benefits, and wide range of applications have made it a popular choice for consumers and businesses alike. While there are some drawbacks to MLC-based storage solutions, its numerous benefits outweigh its limitations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 What is the difference between MLC and SLC?
SLC stands for Single-Level Cell and can store only one bit of data per cell, while MLC stands for Multi-Level Cell and can store multiple bits of data per cell. MLC is more cost-effective than SLC but is less durable and has slower read and write speeds.
Q.2 How is MLC used in SSDs?
MLC is widely used in SSDs due to its cost-effectiveness and performance benefits. MLC-based SSDs are faster and more reliable than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and offer faster boot times, improved system responsiveness, and faster data transfer rates.
Q.3 What is the future of MLC technology?
As the demand for high-capacity, high-performance storage solutions continues to grow, MLC-based SSDs are likely to become even more popular in the future. However, new technologies like 3D NAND flash memory and QLC may also pose a challenge to MLC in the coming years.
Q.4 What are the applications of MLC?
MLC is used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, SSDs, cloud computing, industrial, and automotive.
Q.5 Is MLC better than TLC?
MLC strikes a balance between cost, durability, and performance, making it a popular choice for most applications. However, TLC can store more bits of data per cell, making it more cost-effective than MLC. TLC is also slower and less durable than MLC, making it better suited for applications that require lower endurance and performance.


