EDTA FULL FORM: Properties, Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and Safety Precautions
EDTA, or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, is a compound that has a wide range of applications in various industries. This article will explore the EDTA full form, its properties, uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
Read Other Full Forms
What is EDTA?
EDTA stands for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, which is a synthetic, colorless, water-soluble compound that is widely used in various industries. It is a chelating agent, meaning that it can bind to metal ions and remove them from solutions. EDTA is a versatile compound that has many applications in industrial, medical, and other fields.
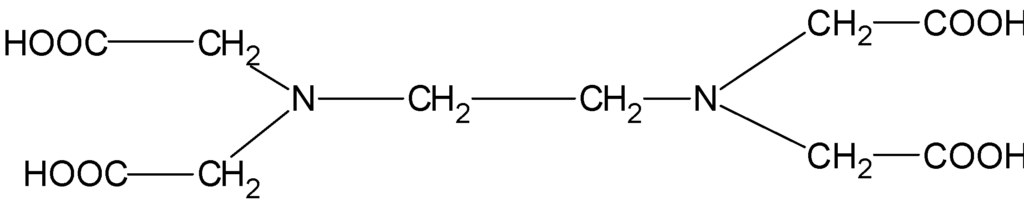
The Properties of EDTA
EDTA is a stable compound that is soluble in water and has a pH of around 4.0. It is also soluble in alcohol, glycerol, and other organic solvents. EDTA has a complex structure, with four carboxylic acid groups and two amine groups. The carboxylic acid groups are responsible for the chelating properties of EDTA.
The Different Forms of EDTA
EDTA is available in various forms, including solid crystals, liquid solutions, and powder. The most common form of EDTA is disodium EDTA, which is a white, crystalline powder. Disodium EDTA is used in many industrial and consumer products, such as soaps, shampoos, and cleaning agents. Other forms of EDTA include tetrasodium EDTA and calcium disodium EDTA.
Uses of EDTA in Industrial Applications
EDTA is widely used in various industrial applications, including:
- Water treatment: EDTA is used to remove metal ions from water, which helps prevent scale buildup and corrosion in pipes and equipment.
- Textile industry: EDTA is used as a dyeing and cleaning agent in the textile industry.
- Food industry: EDTA is used as a preservative in the food industry to prevent discoloration and spoilage.
- Cleaning agents: EDTA is used as a cleaning agent in various household and industrial cleaning products.
EDTA in Medicine and Healthcare
EDTA is also used in medicine and healthcare for various purposes, such as:
- Chelation therapy: EDTA is used to treat heavy metal poisoning by binding to metal ions and removing them from the body.
- Blood collection: EDTA is used as an anticoagulant in blood collection tubes to prevent blood from clotting.
- Treatment of heart disease: EDTA has been used as an alternative therapy for the treatment of heart disease and other circulatory disorders.
Benefits of EDTA
EDTA has several benefits, including:
- Removal of harmful metal ions from the body: EDTA can bind to toxic metal ions, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, and remove them from the body.
- Prevention of plaque buildup: EDTA has been shown to help prevent plaque buildup in arteries, which can reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Antioxidant properties: EDTA has antioxidant properties, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Side Effects of EDTA
While EDTA is generally considered safe, it can cause side effects in some individuals. The most common side effects of EDTA include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Low blood pressure
In rare cases, EDTA can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Kidney damage
- Seizures
- Allergic reactions
It is important to use EDTA under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to follow the recommended dosage and administration instructions.
EDTA Safety Precautions
When using EDTA, it is important to take certain safety precautions, such as:
- Avoiding contact with eyes and skin
- Wearing protective gloves and goggles
- Keeping EDTA away from heat and moisture
- Storing EDTA in a cool, dry place
- Keeping EDTA out of reach of children and pets
It is also important to follow the recommended dosage and administration instructions when using EDTA.
Conclusion
EDTA is versatile and used in many industries. It chelates metal ions and removes them from solutions. Water treatment, textiles, food, and cleaning agents use EDTA. Chelation therapy, blood collection, and heart disease treatment use it. EDTA removes harmful metal ions, prevents plaque, and has antioxidant properties. EDTA can cause side effects in some people, so it’s important to use it under medical supervision and take safety precautions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 Is EDTA safe for human consumption?
EDTA is generally considered safe for human consumption when used in recommended doses and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Q.2 Can EDTA be used to treat heavy metal poisoning?
Yes, EDTA can be used to treat heavy metal poisoning by binding to metal ions and removing them from the body.
Q.3 Can EDTA be used as a preservative in food?
Yes, EDTA is commonly used as a preservative in food to prevent discoloration and spoilage.
Q.4 Does EDTA have any antioxidant properties?
Yes, EDTA has antioxidant properties, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Q.5 What are the most common side effects of EDTA?
The most common side effects of EDTA include nausea, headache, dizziness, diarrhea, and low blood pressure.

