What is the full form of DNA?
DNA full form is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. DNA is made up of a group of molecules that are responsible for passing on materials or genetic instructions from parents to children. DNA is an organic compound with a unique way that its molecules are put together. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have it. In 1869, while studying white blood cells, the Swiss biologist Johannes Friedrich Miescher found and named DNA. Later, James Watson and Francis Crick used evidence from experiments to figure out that the structure of a molecule of DNA is a double helix. Last but not least, it has been shown that DNA is what processes a person’s genetic information.
Read Other Full Forms
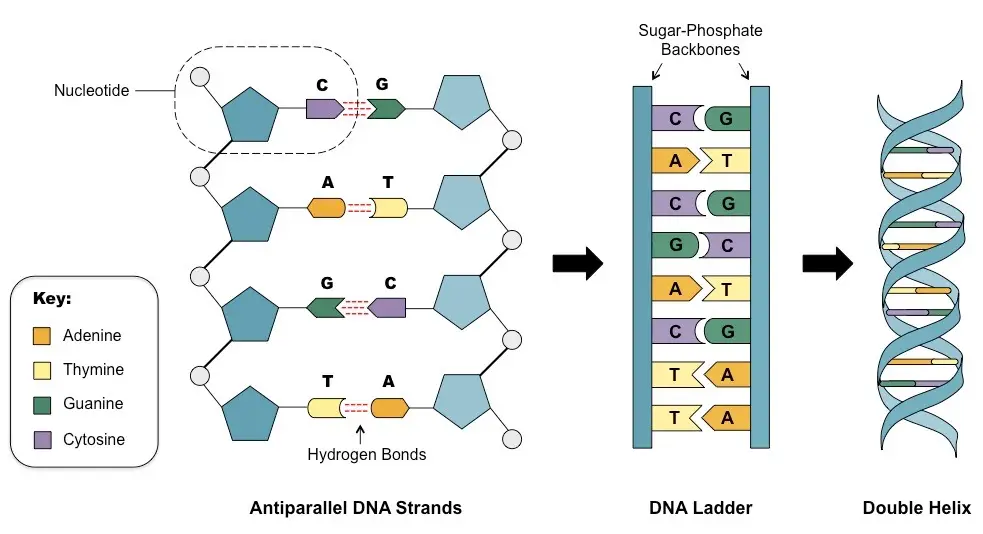
The way DNA is put together could be thought of as a twisted ladder. This shape is called a “double helix,” as shown in the picture above. Nucleotides, which have a carbon-sugar group, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base, are the building blocks of DNA. Each DNA strand is made up of nucleotides that are held together by groups of sugar and phosphate. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C) are the four types of nitrogen bases.
Type of Deoxyribonucleic Acid(DNA)
There are different kinds of DNA.
A – DNA
It is right-handed DNA, and when it dries out, it changes into an A form that protects the DNA when it is doing something active, like binding proteins. Desiccation also gets rid of the DNA solvent.
B – DNA
B – The most common shape for DNA is a right-handed helix. Under normal physiological conditions, most DNA has a shape called type B.
Z – DNA
Z-DNA is a type of DNA in which the double helix winds to the left in a zigzag pattern. It was founded by Alexander Rich and Andres Wang. Z. DNA is found before the starting site of a gene, so it is thought that it controls the gene.
Functions of DNA
- DNA is the genetic material that has all the information passed down in its structure of nitrogen bases.
- From one generation to the next, DNA passes on genetic information from one cell to its daughters.
- Every person has a unique set of genes that don’t fit with those of other people. This property of DNA is used in DNA fingerprinting, which is a way to figure out who someone is based on their DNA.

