Alcohol, phenol, and ether are classes of organic chemicals with a wide range of industrial and residential applications.
You can Read More Chemistry Articles.
- Alcohol is created when a saturated carbon atom forms a covalent bond with a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
- Phenol is produced when a -OH group replaces a hydrogen atom in a benzene molecule.
- Ether is produced by connecting an oxygen atom to two alkyl or aryl groups.
This section will cover the classification of alcohols, phenols, and ethers.
Classification of Alcohol
Depending on the number of connected hydroxyl groups, alcohols can be divided into three categories.
- Monohydric alcohols: They contain one -OH group. Example, CH3CH2-OH
- Dihydric alcohols: They contain two -OH groups. Example, 1,2-Ethandiol.
- Trihydric alcohols: They contain three -OH groups. Example 1,2,3-Propantriol.
Alcohols can be divided into three categories based on the number of carbon atoms that are directly linked to the carbon that is bound to the -OH group.
- Primary alcohols: One carbon atom is directly attached.
- Secondary alcohols: Two carbon atoms are directly attached.
- Tertiary alcohols: Three carbon atoms are directly attached.
Classification of Phenol
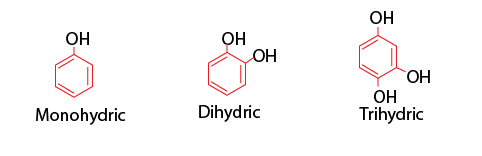
Based on the number of connected hydroxyl groups, phenols can be divided into three categories.
- Monohydric phenols: They contain one -OH group.
- Dihydric phenols: They contain two -OH groups. They may be ortho-, meta- or para- derivative.
- Trihydric phenols: They contain three -OH groups.
Classification of Ether
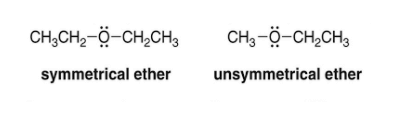
Ether can be divided into two distinct categories based on the nature of the alkyl or aryl groups linked to its oxygen atom.
- Symmetrical ether also called “simple ether,” has the same alkyl or aryl group on both sides of the oxygen atoms. Examples are CH3OCH3, C2H5OC2H5, etc.
- Unsymmetrical ether: Also known as the mixed either, the alkyl or aryl groups connected to the oxygen atoms on either side are not identical. Examples are CH3OC2H5, C2H5OC6H5, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1 How are alcohol and phenols classified?
According to the number of functional groups, alcohol and phenols are categorized as mono-, di-, tri-, or polyhydric. For monohydric alcohols/phenols, one -OH group is present; for dihydric alcohols/phenols, two -OH groups are present; and for tertiary alcohols, three carbon atoms are directly bonded.
Q.2 What are alcohol and ether?
The structure of ether and alcohol resembles that of water. In alcohol, one hydrogen atom of a water molecule is replaced by an alkyl group, whereas both hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups in an ether.
Q.3 What are the uses of ether?
Ether is used in surgery as an anesthetic, as a cooling agent, and as an inert solvent in Grignard reagents.
Q.4 What is simple ether?
A substance is referred to as a simple ether if the alkyl or aryl group linked to each oxygen atom is identical.
Q.5 Which is more soluble, alcohol or phenol?
Due to the creation of hydrogen bonds with water, alcohol, and phenol are both soluble in water. In contrast, phenol is less soluble than alcohol due to the presence of a benzene ring (larger hydrocarbon part).

