What is the full form of ATM?
The ATM full form is an Automated Teller Machine. It is an electro-mechanical machine with automated banking platforms that allow customers to make smooth transactions without the help of a branch representative or teller. At most ATMs, debit card and credit card holders should be able to withdraw cash.
Read Other Full Forms
ATMs are advantageous because they let customers to undertake quick self-service operations, including cash withdrawals, deposits, bill payments, and account-to-account transfers. Typically, the account holder’s bank, the ATM operator, or both pay fees associated with cash withdrawals. By using an ATM operated directly by the account holder’s bank, it is possible to avoid some of these fees. Different regions of the world refer to ATMs as ABM (Automated Bank Machines) or Cash Machines.

History of ATM
In 1967, a Barclays Bank branch in London installed the first automated teller machine, but there are reports of a cash dispenser in Japan from the mid-1960s. In the 1970s, the interbank transaction permitted a consumer to use a card from one bank at the ATM of another bank.
In just a few years, ATMs had established a presence in every major country on the planet. They are currently found in small island states like Kiribati. Globally, there are currently more than 3.5 million ATMs in operation.
Various Types of ATM
There are mainly two types of ATMs.
- Basic units only let clients take out cash and show them their current account balance.
- The more advanced machines allow you to deposit cash, make credit line payments and transfers, and access account information.
Basic Parts of ATM
The ATM is user-friendly. It offers input and output facilities, allowing users to comfortably deposit and withdraw funds. The essential output and input devices of an ATM are located beneath.
Input device
Card reader – The card reader reads the information encoded on the magnetic stripe on the back of the ATM card. Once the card is put in the correct area, the card reader collects the account information and sends it to the server. The cash dispenser dispenses cash based on account information and orders received from the user server.
Keypad – The keypad aids the user in entering the data asked by the machine, including personal identification number, cash amount, receipt required or not, and other information. The PIN is transmitted in an encrypted format to the server.
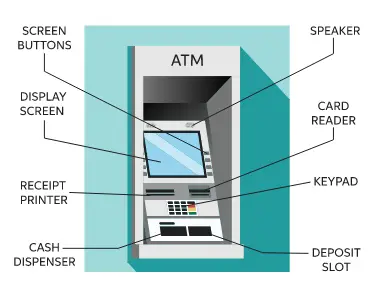
Output Devices
Speaker — The ATM is equipped with a speaker to generate audio input when a button is pressed.
Display Screen — Displays transaction-related information on the screen. It lists the cash withdrawal procedures in sequential sequence. The display could be CRT or LCD.
Receipt Printer — A printed receipt contains transaction-related information. It provides the transaction’s time and date, balance and withdrawal amount, etc.
Cash Dispenser — The cash dispenser is the ATM’s most important output device, as it dispenses cash. The ATM’s very accurate sensors enable the cash dispenser to dispense the exact amount of cash the customer requires.
Working Principle of ATM
To initiate the operation, plastic ATM cards must be inserted into ATMs. On certain machines, you must drop your cards, while others demand card changing. The magnetic stripe on these ATM cards contains your account information and other security information. When you lose or replace your card, the computer receives account information and demands your PIN number. Once the authentication is genuine, cash transactions will be permitted by the machines.
Functions OF ATMs
- Deposit of cash
- Withdrawal of cash
- Transfer of cash
- Accounts details
- Mini statement
- Regular payment of the bill
- Account balance details
- Recharge of prepaid mobile
- Change the pin code
Advantages of ATM
- The ATM service is available 24/7.
- It minimizes the workload of bank employees.
- For travellers, ATMs are more useful.
- The ATM provides service without error.

