What is Ammonium Oxalate (C2H8N2O4)?
Ammonium Oxalate is an inorganic compound with the formula C2H8N2O4. Also known as diammonium oxalate and diammonium salt.
You can Read More Chemistry Articles.
Ammonium Oxalate is an ammonium-containing oxalate salt. Ammonium Oxalate is a very acidic dicarboxylic compound. The ratio of ammonium ions to oxalate ions in this molecule is 2:1.
Normal conditions produce colorless to white salt. The substance is odorless and nonvolatile. It slowly dissolves in water. It occurs naturally in numerous plants and vegetables.
Structure of Ammonium Oxalate – C2H8N2O4
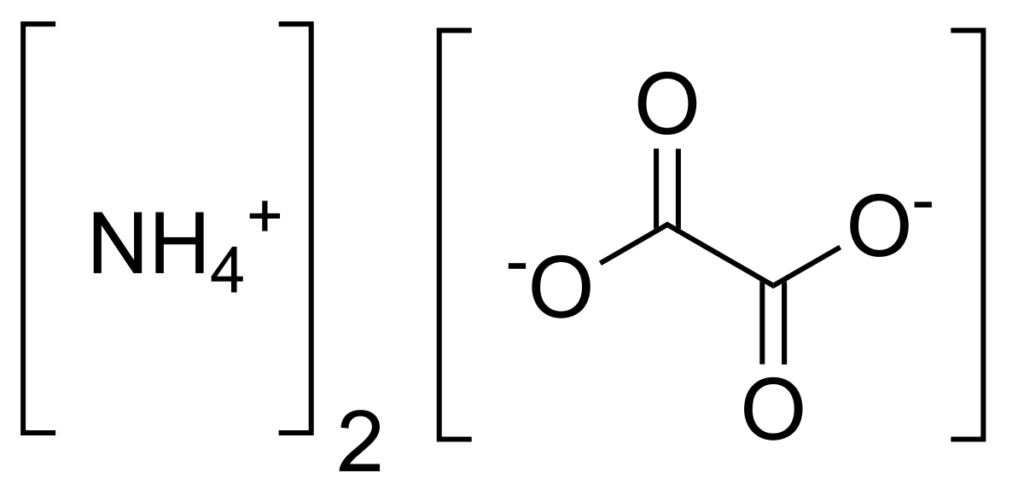
Properties of Ammonium Oxalate – C2H8N2O4
| C2H8N2O4 | Ammonium Oxalate |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 124.1 g/mol |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 at 65.3° F |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting Point | 70°C |
Under ordinary conditions, it is a colorless crystalline solid with a melting point of 374.5K in hydrated form and 463K in anhydrous form. It is soluble in water and alcohol but ether-insoluble.

Uses of Ammonium Oxalate
- It is formed in vertebrate bodies by the metabolism of ascorbic acid or glyoxylic acid.
- Oxammite is the mineral form of ammonium oxalate.
- It acts as a reducing agent.
- It is used as a chemical reagent.
- As an anticoagulant, it’s used to preserve blood outside the body.
Health Hazards Associated with Ammonium Oxalate
- Ingestion or excessive inhalation of ammonium oxalate dust results in systemic toxicity.
- Contact with the eyes is irritating. Contact with the skin results in serious burns.
- Absorbed via the skin. Ammonium oxalate is irritating to the skin, and a physician should be seen if someone gets signs or symptoms and suspects they are due to exposure.
Structure, physical and chemical properties of C2H8N2O4 explained by the specialists at Utopper.com.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1 What are the uses of ammonium oxalate?
In blood tests, ammonium oxalate is used to block or decrease the coagulation of blood plasma. This chemical can also be complexed with certain metals to determine the concentration of lead or calcium ions in blood, among other analytes.
Q.2 Is ammonium oxalate acidic or basic?
Ammonium oxalate is typically an acidic substance. The acidity is dependent on the concentration of oxalic acid. Soil analysis can be performed with acid ammonium oxalate, which can be produced by acidifying ammonium oxalate to pH 3 with oxalic acid.
Additionally, it can be utilized to recover aluminum and iron from materials with poor crystalline structure.
Q.3 Is ammonium oxalate ionic or covalent?
The ammonium cation and the oxalate anion form an ionic connection within ammonium oxalate molecules. Ammonium oxalate is therefore an ionic compound. In addition, this molecule consists of two polyatomic ions.
Ammonium is a polyatomic ion composed of hydrogen and nitrogen. Additionally, the oxalate anion is a polyatomic ion composed of oxygen and carbon atoms.
Q.4 How can ammonium oxalate be prepared?
Typically, the reaction between oxalic acid and ammonium carbonate in water is required for the production of ammonium oxalate. 100 grams of oxalic acid can be dissolved in 800 milliliters of water and then neutralized with 83 grams of ammonium carbonate to produce ammonium oxalate (the solution can be gently warmed before the neutralization).
Q.5 Is ammonium oxalate soluble in water?
Like the majority of ionic ions, ammonium acid is soluble in water. Typically, this ionic molecule exists as a monohydrate salt.

