What is Ammonium Ion?
Ammonium Ion has the chemical formula NH4+ and is a polyatomic cation.
A cation is an electron-deficient and positively charged substance. A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalently linked group of two or more atoms or a metal complex with a net charge larger than zero.
You can Read More Chemistry Articles.
In ammonium, four hydrogen atoms are covalently bound to a single nitrogen atom, with a total charge of +1.
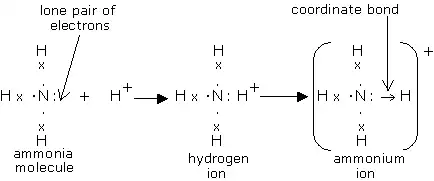
Formation of Ammonium Ion
The ammonium ion is generated when a neutral ammonia molecule NH3 is protonated or acquires an extra positively charged hydrogen atom.
NH3 + H+ → NH4+
In ammonia, nitrogen is a core atom with 5 electrons in its valence shell, 3 of which are shared with 3-H atoms, and 1 pair of lone electrons.
It is an electron-rich species (nucleophile) because it has an unshared electron pair (lone pair electron) and can donate it to another atom (electrophile). As a result, ammonia is a donor, and an ammonium ion is generated when an ammonia atom transfers its lone pair to a proton.
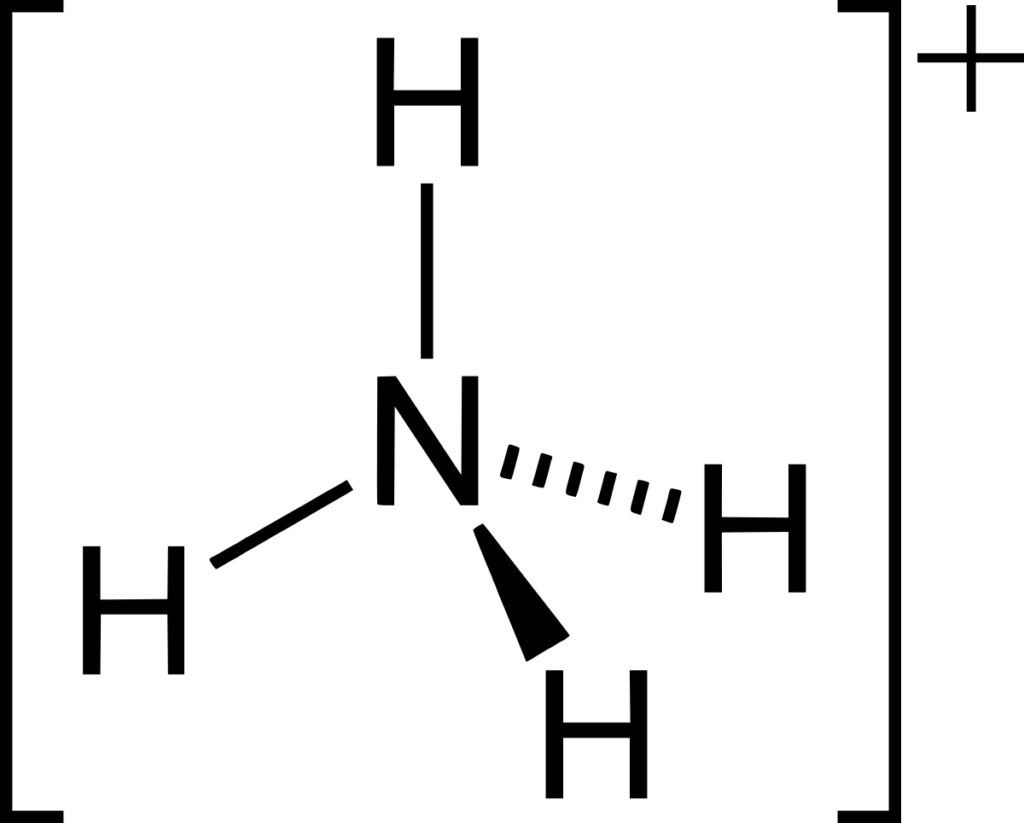
Structure and Bonding of Ammonium Ion
As polar covalent bonds, each of the four N–H bonds is identical. The ion shares the same electron configuration as methane and borohydride and has a tetrahedral shape.
Properties of Ammonium Ion
| Name of Molecule | Ammonium ion |
| Chemical formula | [NH4]+ |
| Molar mass | 18.039 g/mol |
| Conjugate base | Ammonia(NH3) |
| IUPAC Name | azanium |
| Nature | Weak acid |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.25 |
- All ammonium salts are white and water-soluble.
- The ammonium ion acts chemically similar to the ions of alkali metals, particularly the potassium ion, which has almost the same size.
- Ammonium ion works as a mild acid in aqueous solutions because it degrades in water into ammonia and a hydrogen ion.
[NH4]+(aq) ⇋ NH3(aq) + H+(aq)
Ammonium Salts
The formula for ammonium salts is (R)4N+A–, where R denotes a hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl group and A represents an anion.
The salts are referred to as quaternary ammonium salts when R is alkyl or aryl. The ammonium quaternary cations are continuously charged regardless of the pH of the solution. The majority of ammonium salts are substantially dissociated and water-soluble. Ammonium salts are used to create cleaning agents, food additives, diuretics, surfactants, antistatic agents, and disinfectants. It has been demonstrated that they have antibacterial characteristics. Ammonium quaternary salts sustain intracellular osmotic pressure.
Long alkyl chain quaternary ammonium compounds, such as benzalkonium chloride, cetylpyridinium chloride, dofanium chloride, benzethonium chloride, methyl benzethonium chloride, cetalkonium chloride, and didecyldimethylammonium chloride, exhibit antibacterial, fungicidal, and antiviral properties. Since anionic detergents destroy these quaternary ammonium compounds, hard water should not be used with them. They are frequently used as disinfectants.
In organic synthesis, quaternary ammonium salts are frequently used as phase transfer catalysts (PTCs), which catalyze the reaction between ionic and organic reactants. As a plant growth regulator, chlormequat chloride inhibits gibberellin synthesis.
Applications
- Ammonium ions are an animal metabolic waste. Fish and aquatic invertebrates excrete this substance directly into the water. During the urea cycle, it is transformed to urea in mammals, sharks, and amphibians because urea is less poisonous and can be stored more efficiently.
- Birds, reptiles, and terrestrial snails transform metabolic ammonium into uric acid, which is solid and may therefore be expelled with minimum water loss.
- Ammonium is an essential source of nitrogen for numerous plant species, especially those that thrive in hypoxic soils. However, it is hazardous to most crop species and is rarely utilized as the primary supply of nitrogen.
- The ammonium ion [NH4]+ is crucial for acid-base equilibrium in the body.
How to Detect Ammonium Ion?
A solution’s ammonium ions can be determined by adding a diluted sodium hydroxide solution and warming it slowly. If ammonium ions are present, they will be transformed to ammonia gas. The odor of ammonia is unmistakable and overpowering. Wet red litmus paper and universal indicator paper are also colored blues.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ammonium Ion
Q.1 Why is ammonium an ion?
When an ammonia molecule, NH3, combines with a proton, H+ cation, the unshared or lone pair of electrons in the N-atom create a coordinate or dative bond with the H+, generating ammonium ion.
Q.2 What is the formal charge on ammonium ion?
The formal charge linked with ammonium ion is +1.
Q.3 Which test is a confirmatory test for ammonium ion?
Adding an alkaline hydroxide to the solution and heating it will establish the existence of ammonium ions if the solution emits a gas with a distinctive odor. In interaction with alkali hydroxide, ammonium ions produce ammonia gas.
Q.4 Where are ammonium ions found?
Ammonium ions are present in diluted ammonia solution and all ammonium salts, such as ammonium chloride.
Q.5 Is ammonium ion acidic or basic?
An acid is a substance that creates protons when dissolved in water. When ammonium ion is dissolved in water, it dissociates into NH3 and H+ ions. The ammonium ion is therefore a mild acid.

