What is Aluminium Phosphate?
Aluminium phosphate is produced by exposing soluble aluminium salts to alkaline conditions; it is composed of hydrated aluminium orthophosphate with the formula AlPO4.
Extremely viscous solutions of aluminum phosphate tend to form polymeric aggregates, and equilibrium is reached extremely slowly. Slowly, it interacts with stomach acid to produce soluble aluminum salts and phosphoric acid. Aluminium hydroxide absorbs bile acids more strongly than magnesium hydroxide.
You can Read More Chemistry Articles.
Other names: Aluminium monophosphate
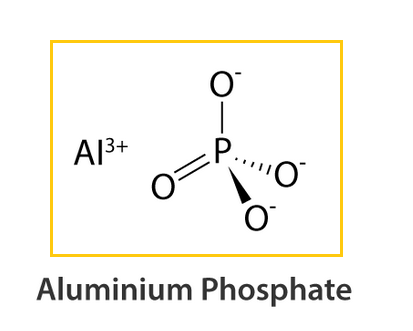
Aluminium Phosphate Structure – AlPO4
Properties of Aluminium Phosphate – AlPO4
| AlPO4 | Aluminium Phosphate |
| Density | 2.57 g/cm³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 121.9529 g/mol |
| pH | 3.0 to 7.5 |
| Melting Point | 1,800 °C |
| Chemical Formula | AlPO4 |
Physical Properties of Aluminium Phosphate – AlPO4
| Odour | foul odour |
| Appearance | White,crystalline powder |
| Complexity | 36.8 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 4 |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
Chemical Properties of Aluminium Phosphate – AlPO4
The reaction between aluminium phosphate and hydrochloric acid produces phosphoric acid and aluminium trichloride.
AlPO4 + 3HCl → AlCl3 + H3PO4
The reaction between magnesium chloride and aluminum phosphate produces magnesium phosphate and aluminum trichloride.
2AlPO4 + 3MgCl2 → Mg3(PO4)2 + 2AlCl3
Uses of Aluminium Phosphate – AlPO4
Aluminum phosphate tablets are authorized by the British Pharmacopoeia, and each tablet includes 500 mg of dried aluminum phosphate that is acceptable for peppermint flavor.
Beneficial antacids are used in patients with substantial phosphate loss due to the usage of aluminum salts.
Used as an additive in the production of vaccines to boost immunogenicity
In a water suspension of hydroxy aluminium carbonate and orthophosphoric acid, aluminium phosphate-carbonate gels were employed.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1 What is the use of aluminum phosphate?
Aluminum Phosphate is a crystalline, odorless, white solid that is frequently employed in liquid or gel form. It is utilized in the manufacture of ceramics, dental cements, cosmetics, paints, paper, and pharmaceuticals.
Q.2 What is the purpose of aluminum in food?
As a firming agent, raising agent, stabilizer, anti-caking agent, and coloring agent, etc., aluminium-containing food additives have been used in food processing for over a century, and in many countries, their usage is approved. Aluminium is also naturally contained in food.
Q.3 What are the disadvantages of Aluminium foil?
Even if aluminum cans are recyclable, they nevertheless pose a threat to the environment and the public’s health. Disadvantages One of the downsides of utilizing aluminum foil is that laminated foils cannot be recycled like regular foils.
Q.4 Where does aluminum phosphate come from?
It occurs naturally as the mineral berlinite. There are numerous synthetic versions of aluminum phosphate known.
Q.5 Why do we need phosphate?
The mineral phosphorus is included in the charged particle (ion) phosphate. Phosphorus is required for bone and tooth formation and repair, nerve function, and muscle contraction. Approximately 85 percent of the phosphorus in phosphate is found in bones.

