Aldol Condensation Questions and Answers: Aldol condensation is an organic reaction in which an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to produce a β-hydroxy ketone or β-hydroxy aldehyde, which is then dehydrated to yield a conjugated enone. Aldol condensation is necessary for organic synthesis because it enables the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
You can Read More Chemistry Articles.
When aldehydes and ketones with at least one -hydrogen are treated with dilute alkali (which acts as a catalyst), β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) and β-hydroxy ketones (ketol) are produced, respectively. The term for this reaction is aldol condensation.
Aldol Condensation Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Q1. Aldol condensation takes place in-
a.) Aldehyde
b.) Ketone
c.) Both (a) and (b)
d.) None of the above
Correct Answer. (c.) Both (a) and (b)
Q2. Aldol condensation will not take place in-
a.) HCHO
b.) CH3CHO
c.) CH3COCH3
d.) CH3CH2CHO
Correct Answer- (a.) HCHO
Q3. The catalyst used in the aldol condensation reaction can be-
a.) acid
b.) alkali
c.) Both (a) and (b)
d.) None of the above
Correct Answer- (c.) Both (a) and (b)
Q4. Which of the following is/are correct conditions for aldol condensation to take place?
a.) Presence of at least one ɑ–hydrogen.
b.) An alkali as a catalyst.
c.) Aldol condensation takes place only in aldehydes and ketones.
d.) All of the above.
Correct Answer. (d.) All of the above
Q5. Aldol condensation will not be observed in?
a.) Chloral
b.) Phenyl acetaldehyde
c.) Hexanal
d.)Ethanal
Correct Answer- (a.) Chloral
Q6. Aldol condensation does not involve formaldehyde. Why?
Answer. Formaldehyde does not contain an ɑ-hydrogen atom. As a result, it does not participate in aldol condensation.
Q7. What type of aldehydes undergo Aldol condensation?
Answer. Aldol condensation occurs when an aldehyde contains an ɑ–hydrogen atom.
Q8. Describe and illustrate
a) Aldol condensation.
b) Cross Aldol Condensation
Answer.
a) Aldol condensation: This occurs when two molecules of aldehydes or ketones with ɑ–hydrogen atoms are treated with dil. NaOH condenses to form β-hydroxy aldehydes or β–hydroxy ketones.
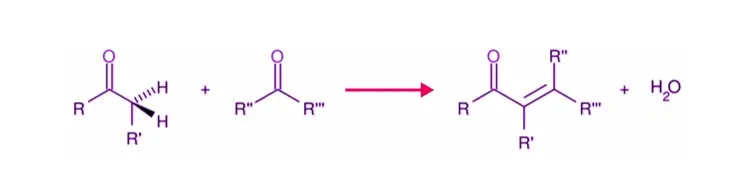
b) Cross Aldol Condensation: Cross aldol condensation occurs when aldol condensation occurs between two different aldehydes or ketones.
Q9. What role does NaOH play in aldol condensation?
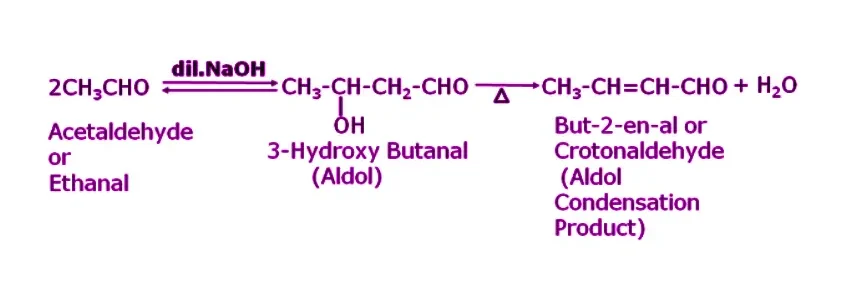
Answer. Since NaOH contains an alpha-hydrogen atom, it undergoes self-condensation, resulting in the formation of β–hydroxy aldehyde (an aldol), specifically 3-Hydroxy butanal. Upon further heating, this compound will lose a water molecule, producing the aldol condensation product Crotonaldehyde or But-2-en-al.
Q10. What’s the difference between an aldol reaction and an aldol condensation?
Answer. The Aldol Reaction occurs when a carbonyl compound enolates with aldehydes and ketones to form a β–hydroxy carbonyl compound. If conditions result in subsequent dehydration to form the ɑ,β–unsaturated compound, the reaction is known as the Aldol Condensation.
Q11. Explain the Aldol condensation mechanism.
Answer. The Aldol condensation mechanism is as follows-
- Aldol condensation is an organic reaction in which an enolate ion reacts with a carboxyl compound to generate β–hydroxy aldehyde or β–hydroxy ketone.
- Hydroxide acts as a base, resulting in the movement of the acidic a-hydrogen and the formation of the reactive enolate ion. This represents an acid-base reaction.
- The nucleophilic enolate ion attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde. The intermediate of this nucleophilic addition reaction is an alkoxide.
- The alkoxide deprotonates the water molecule to produce hydroxide and β–hydroxy aldehyde.
Q12. What happens when acetaldehyde is made to react with dilute NaOH?
Answer. When acetaldehyde is treated with dil. NaOH, it undergoes self-condensation because it contains an alpha-hydrogen atom in its compound resulting in the formation of 3-Hydroxy butanal. This compound upon further heating will eliminate a molecule of water which will result in the formation of an aldol condensation product namely crotonaldehyde or But-2-en-al.
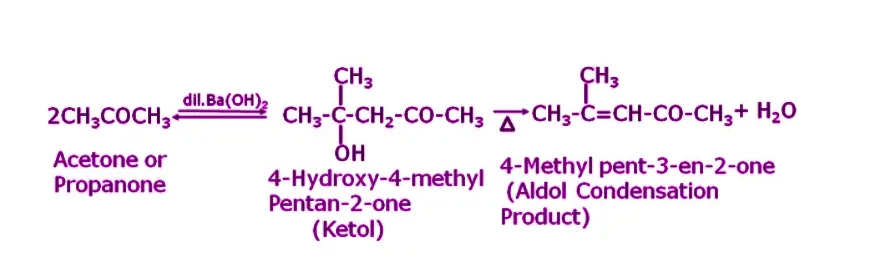
Q13. Explain the reaction when acetone is treated with an alkali?
Answer. When acetone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2, it undergoes self-condensation due to the presence of an alpha-hydrogen atom in its molecule, resulting in the formation of 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl Pentan-2-one. This compound, upon further heating, will lose a water molecule, resulting in the formation of 4-methyl pent-3-en-2-one, an aldol condensation product.
Q14. What is crossed aldol condensation?
Answer. Crossed aldol condensation is a type of aldol condensation in which two dissimilar carbonyl compounds (each containing alpha hydrogens) react together. Up to four different products can be formed in such reactions.
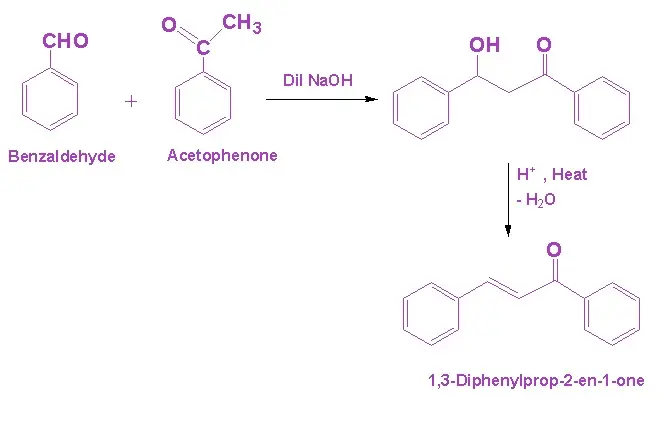
Q15. Explain the reaction of Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.
Answer. In the presence of dil. NaOH, the reaction between benzaldehyde and acetophenone undergoes cross-aldol condensation. Since, benzaldehyde lacks alpha hydrogen in this reaction, acetophenone undergoes aldol condensation to form β-hydroxy ketone. Dehydration also results in the formation of the, α, β – unsaturated ketone.