What are Acid Bases and Salts
The presence of acids and bases in food gives it its sour and bitter taste. Acids have a sour taste and turn blue litmus red, whereas bases have a bitter taste and convert red litmus blue. Similar to litmus is the natural indicator turmeric. The reaction between an acid and a base yields a salt, a neutral molecule.
Definition: Acids are substances that add protons or take electrons away. It dissociates in an aqueous solution into H+ ions. A base is a substance that donates electrons or removes protons. It dissociates into OH– ions in an aqueous solution.
Acid Bases and Salts MCQ Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Q-1: Which of the following is the correct classification of Dolomite?
- An acid salt
- A mixed salt
- A normal salt
- A double salt
Answer: d) double salt
Explanation: A double salt is a crystalline salt with content of a mixture of two simple salts but a distinct crystal structure. Dolomite is a double salt consisting of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) salts.
Q-2: Acetic acid is a weak acid because
- Its aqueous solution is acidic
- It is highly ionized
- It is weakly ionized
- It contains the COOH group.
Answer: c) It is weakly ionized
Explanation:
In an aqueous solution, a weak acid is one that ionizes just minimally. Acetic acid (found in vinegar) is a highly common weak acid because it doesn’t dissociate much in solution, Its ionization may be seen below.
Q-3: Butyric acid is found in
A. Rancid butter
B. Rancid cake
C. Stings of bees
D. All of these
Answer: B) Rancid cake
Q-4: Which of the following is not an amphiprotic species?
- HCO3–
- HPO42-
- OH–
- H2PO42-
Answer: c) OH–
Explanation: Amphiprotic ions are those ions which can gain or lose hydrogen ions.
Except OH–, all other species are amphiprotic in nature. OH– can gain a proton to form H2O but it cannot lose. Hence it is not amphiprotic.
Q-5: Three reactions involving H2PO4– are given below:
i) H3PO4 + H2O → H3O+ + H2PO4–
ii) H2PO4–+ H2O → HPO42- + H3O+
iii) H2PO4– + OH–→ H3PO4 + O2-
In which of the following above H2PO4– act as an acid?
- ii only
- i) and ii)
- iii) only
- i) only
Answer: a) ii only
Explanation: An acid is a material that loses protons and we can see that, only in ii) H2PO4– is donating a proton to water. Thus it acts as an acid.
Q-6: Which of the following compound is most acidic?
- Cl2O7
- P4O10
- SO3
- B2O3
Answer: a) Cl2O7
Explanation: Acidic strength is the tendency of a molecule/compound to liberate protons. In case of proton deficient compounds, acidic strength is governed by the positive oxidation state of the central atom. More is the value of the positive oxidation state, more is the acidic strength.
The oxidation states of Cl,P,S and B are +7,+5,+6 and +3 respectively.
This shows that Cl2O7 is the most acidic.
Q-7: Identify the basic salt from the following.
- Na2CO3
- NaNO3
- KCl
- NH4Cl
Answer: a) Na2CO3
Explanation: There are three main classifications of salts:
Acidic Salt: A salt that is formed by the neutralization of strong acid and weak base.
Basic Salt: A salt that is formed by the neutralization of a strong base and weak acid.
Neutral Salt: A salt that is formed by the neutralization of strong acid and strong base.
Q-8: Which of the following can be considered as an example of olfactory indicators?
- Onion
- Methyl orange
- Turmeric
- China rose
Answer: a) Onion
Explanation: A substance whose smell varies when it is mixed with an acidic or basic solution is said to be an olfactory indicator. In the laboratory, olfactory indicators can be used to determine whether a solution is a basic or an acid, a procedure known as olfactory titration.
Some common examples are Onion, vanilla, clove oil etc.
Q-9: The pH of a solution obtained by mixing 50.00 mL of 0.20 M weak acid HA (Ka = 10-5) and 50.00 mL of 0.20M NaOH at room temperature is
- 2
- 3
- 5
- 9
Answer: d) 9
Explanation: Salt is formed when equal amounts of acids and bases react neutralizing the effect of each other.
Here, weak acid(HA) reacts with a strong base(NaOH) in the same proportion, thus a basic salt is formed.
Step-1- Calculate the moles of acid
Moles of acid = Molarity × V(L)
= (0.20 mol/L)×(0.05L)
= 0.01 mol
Step-2- Calculate the moles of base
Moles of acid = Molarity × V(L)
= (0.20 mol/L)×(0.05L)
= 0.01 mol
The formula used for calculating pH of a basic salt is:
pH= ½( pKa + pKw + log c)
As pKa = -logKa
= -log(10-5)
= 5
At room temperature, pKw = 14
‘C’ is the concentration of the salt (NaA)
Let us consider a reaction,
| HA | + NaOH → | NaA + H2O | |
| Initial | 0.01mol | 0.01mol | – |
| After reaction | – | – | 0.01 mol |
Total volume(L)= (0.05+0.05)L= 0.1L
C= Moles of NaA/Total volume
= 0.01/0.1
= 0.1M
Substituting the values in the formula,
pH= ½(5+14+log(0.1)
= 9
Q-10: The pH of a solution prepared from 0.005 mole of Ca(OH)2 in 100cc water is
a)10
b) 12
c) 11
d) 13
Answer: d) 13
Explanation:
Step-1-Calculate the [OH–] in the solution
We know that,
Molarity = Number of moles/Volume(in L)
[OH–] = 0.005 mol /0.1L
= 0.05 M
Since there are two OH– ions, therefore [OH–] = 2× 0.05
= 0.1 M
Note: 100cc =100mL = 0.1L
Step-2– Calculate pOH
pOH = -log[OH–]
= -log(0.1)
= 1
As, pKw = pH +pOH
Also, at room temperature, pKw = 14
Substituting the values,
14= pH+1
pH= 13
Hence, the pH of the solution is 13.
Q-11: The pH of 0.1 M solution of the following salts increases in the order
- NaCl<NH4Cl<NaCN<HCl
- HCl< NH4Cl<NaCl<NaCN
- NaCN<NH4Cl<NaCl<HCl
- HCl<NaCl<NaCN<NH4Cl
Answer: HCl< NH4Cl<NaCl<NaCN
Explanation: pH is the measure of whether the solution is acidic, basic or neutral on the basis of its value.
With a pH of 7, salts of a strong acid and a strong base are neutral. Salts of a strong acid and weak base, on the other hand, are acidic with a pH less than 7, and salts of a strong base and weak acid are basic with a pH greater than 7.
NaCl is the salt of strong acid( HCl) and strong base (NaOH) which makes it overall neutral
NH4Cl is the salt of strong acid (HCl) and weak base(NH4OH ) which makes it acidic but not more than HCl.
NaCN is the salt of a weak acid (HCN) and strong base (NaOH) which makes it basic.
HCl is a strong acid.
Thus, the correct order of pH is
HCl< NH4Cl<NaCl<NaCN
Q-12: Which of the following is not a use of Bleaching powder?
- Bleaching agent
- Oxidising agent
- Used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
- Disinfectant
Answer: c) Used in soda-acid fire extinguishers
Explanation: Bleaching powder is represented as CaOCl2.
There are many applications of Bleaching powder:
(i) It is used for bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry.
(ii) bleaching wood pulp in paper factories and for bleaching washed clothes in laundry.
(iii) as an oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
(iv) to make drinking water free from germs.
Q-13: What is the correct formula of Plaster of Paris?
- CaSO4
- CaSO4.1/2H2O
- CaSO4.2H2O
- Ca(OH)2
Answer: b) CaSO4.1/2H2O
Explanation:
Plaster of Paris is a material used by doctors to maintain shattered bones in the proper position. Plaster of Paris is a white powder that transforms into gypsum when mixed with water, resulting in a hard solid mass.
Its chemical name is calcium sulphate hemihydrate with the chemical formula of CaSO4.1/2H2O.
Q-14: Which of the following salts do not contain water of crystallisation?
a) Baking Soda
b) Gypsum
c) Red vitriol
d) Copper sulphate
Answer: a) Baking soda
Explanation: Water molecules found inside crystals are known as water of crystallisation or water of hydration in chemistry.
Gypsum has a chemical formula of CaSO4.2H2O
Baking soda has a chemical formula of Na2CO3
Red vitriol has a chemical formula of CoSO4.7H2O
Copper sulphate has a chemical formula of CuSO4.5H2O
Q- 16. pH scale of a neutral solution is
A. 14
B. 7
C. 10
D. 12
Answer: B) 7
Q-17 Which of the following statements is correct about an aqueous solution of an acid and of a base?
(i) Higher the pH, stronger the acid
(ii) Higher the pH, weaker the acid
(in) Lower the pH, stronger the base
(iv) Lower the pH, weaker the base
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer: d) (ii) and (iv)
Explaination: Reason: Stronger the acid, lesser is the pH. The stronger the base, the higher is the pH.
Q-18 Lime water is
(a) CaO (b) Ca(OH)2 (c) CaCO3 (d) CaCI2
Answer: B) Ca(OH)2
Q-19 Alkalis are
(a) acids, which are soluble in water
(b) acids, which are insoluble in water
(c) bases, which are insoluble in water
(d) bases, which are soluble in water
Answer: D) bases, which are soluble in water
Q-20. Lime water reacts with chlorine to give
(a) bleaching powder
(b) baking powder
(c) baking soda
(d) washing soda
Answer: c) baking soda
Explaination:
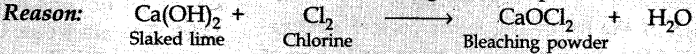
Q-21. Nettle sting is a natural source of which acid?
(a) MetiWanoic acid
(b) Lactic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Tartaric acid
Answer: a) Metiwanoic acid
Q-22. Tooth enamel is made up of
(a) calcium phosphate
(b) calcium carbonate
(c) calcium oxide
(d) potassium
Answer: a) calcium phosphate

