What is Acetylene?
Acetylene is also known by the names Ethyne, Narcylen, and vinylene. As both a chemical building block and a fuel, it is widely employed. It is treated as a solution in its pure form since it is unstable in its natural state. It is an unsaturated molecule since its two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond. It is a colorless, flammable gas that is widely employed as a fuel in oxyacetylene welding and metal cutting, as well as a raw ingredient in the synthesis of numerous organic compounds and plastics. C2H2 is its chemical formula.
As manufactured from calcium carbide, acetylene typically contains residues of phosphine that impart an unpleasant, garlic-like odor. With the release of heat, acetylene can be broken down into its component atoms. Depending on the circumstances, the decomposition might or might not cause an explosion. Pure acetylene under pressures exceeding approximately 15 pounds per square inch, whether in liquid or solid form, explodes violently.
Acetylene Structure – C2H2
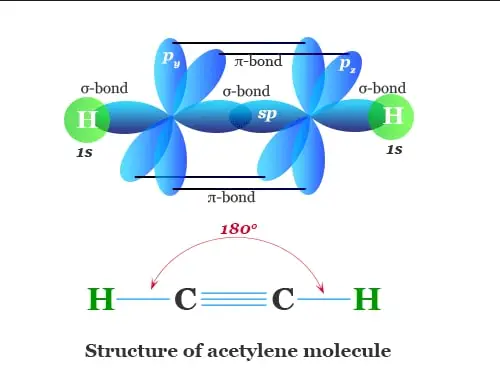
Properties of Acetylene – C2H2
| C2H2 | Acetylene |
| Molecular weight of C2H2 | 26.038 g/mol |
| Density of Acetylene | 1.097 kg/m3 |
| Boiling point of Acetylene | -84.7°C |
| Melting Point of Acetylene | −80.8 °C |
Chemical Properties of Acetylene (C2H2)
Reaction with HBr
The result of reacting acetylene with HBr is ethylidene bromide.
Reaction with sodium metal
The reaction between sodium and acetylene produces sodium hydro acetylide and hydrogen.
Na + C2H2 → NaHC2 + H2
Reaction with HCl
When acetylene and Hydrochloric Acid HCl combine, CH3CHCl2 is produced.
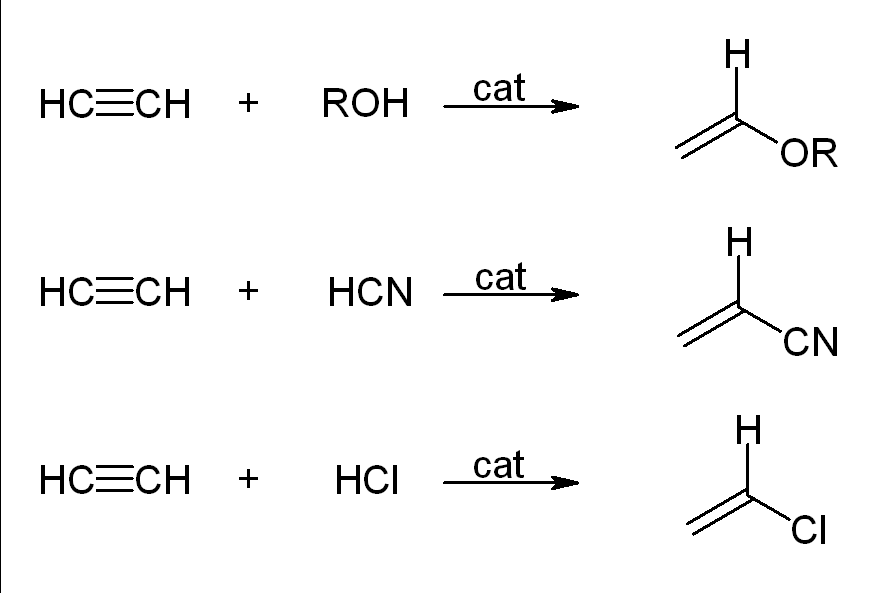
Other Reactions of Acetylene
Vinylation reactions
H−X chemicals combine across the triple bond in vinylation reactions. The addition of alcohols and phenols to acetylene produces vinyl ethers. Thiols give thioethers for vinyl. Similarly, 2-pyrrolidone and carbazole are industrially converted into vinylpyrrolidone and vinylcarbazole.
Carbonylation
Walter Reppe observed that acetylene reacts with a large variety of industrially significant compounds in the presence of catalysts.
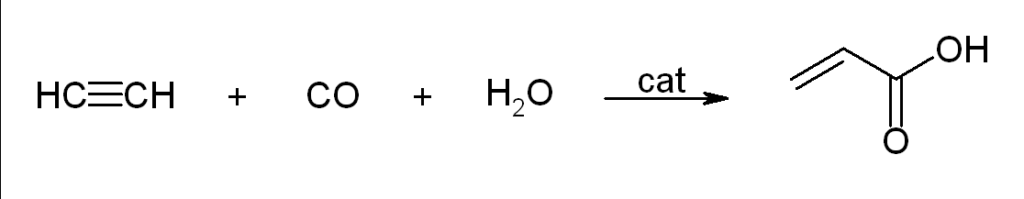
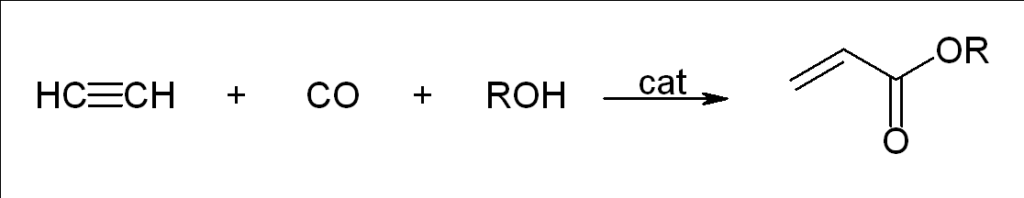
Acetylene Molecular Formula
The Molecular Formula of Acetylene is – C2H2
Acetylene Uses
- Acetylene is used in brazing.
- Used in the glass industry.
- Used in the manufacturing of synthetic rubber.
- Used in soldering metals.
- Used as an additive to preserve food.
- Used to precipitate metals.
- Used to manufacture acetic acid.
- Used as a feedstock in the manufacturing of acrylonitrile.
- Used in the carburization of steel.
- Used as a fuel additive.
Production of Acetylene
Since 1950, this chemical has been produced through the incomplete combustion of CH4 (methane). Until 1983, approximately 4,000,000 tonnes were produced.
In 1862, Friedrich Wohlerthe discovered a chemical process that enabled its preparation. Following is the hydrolysis of calcium carbide reaction:
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
Using an electric arc furnace, the aforementioned reaction takes place at a very high temperature of roughly 2000 °C.
Health Hazards
Those who come into touch with this substance may experience headaches, loss of consciousness, and vertigo. In the presence of a larger concentration of ethyne, choking can result in death.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q.1 What is acetylene used for?
Welding and cutting procedures employ acetylene. Using acetylene for welding is referred to as cutting oxy-fuel or cutting coal. This process is used to cut or weld materials that require temperatures of up to 3,500 degrees Celsius (6,330 degrees Fahrenheit). Acetylene can produce the brightest flame of all gases.
Q.2 Are ethylene and acetylene the same?
The molecules ethylene and acetylene are both hydrocarbons. They are, respectively, the simplest alkene and alkyne. Unlike ethylene, which occurs naturally, acetylene is produced by distinct technical processes.
The principal distinction between ethylene and acetylene is that ethylene is an alkene and acetylene is an alkyne.
Q.3 Is acetylene a toxic gas?
In standard industrial practice, acetylene is not regarded as a significant hazardous danger. However, it poses a significant fire and explosive risk. The literature contains numerous tales of deaths caused by acetylene explosions. Simply put, acetylene is an asphyxiant.
Q.4 How is acetylene manufactured?
There are three ways to produce acetylene: the interaction of water with calcium carbide, the passage of a hydrocarbon through an electric arc, or the partial combustion of methane with air or oxygen.
Q.5 Is acetylene corrosive to metal?
Acetylene in its purest form is odorless and colorless. In addition to its other activities, acetylene is now recognized to suppress the top-line corrosion that typically occurs in gas pipelines. As a result of its high volatility, it can be sprayed as a corrosion inhibitor.Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs

