What is the Full form of IC?
The IC Full Form is an integrated circuit, also called a chip, microchip, or microelectronic circuit is a semiconductor wafer on which thousands or millions of tiny resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors are made. An IC can work as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, counter, logic gate, computer memory, microcontroller, or microprocessor.
All modern electronics are made up of ICs, which are the basic building blocks. As the name suggests, it is a system made up of many small, interconnected parts that are built into a thin layer of semiconductor material (usually silicon crystal).
History of IC
- The Loewe 3NF vacuum tube from the 1920s was one of the first devices to try to combine several parts into one (like ICs do today). Unlike ICs, it was made to avoid taxes because radio receivers in Germany were taxed based on how many tube holders they had. It made it possible for radio receivers to only have one tube holder.
- In 1949, a German engineer named Werner Jacobi (Siemens AG) filed a patent for a semiconductor amplifying device that looked like an integrated circuit. It had five transistors on a common substrate and was set up as a three-stage amplifier. Jacobi said that his patent could be used to make small, inexpensive hearing aids.
Types of IC ( By Generations )
- Integrated circuits can be put into three main categories: analogue, digital, and mixed-signal, which use both analogue and digital signals on the same IC.
- SSI – Small Scale Integration – means that each IC or cube has between 1 and 100 transistors.
- MSI – Medium Scale Integration – means that each IC or cube has between 1,000 and several hundred thousand transistors.
- VLSI – Very Large Scale Integration – means that each IC or cube has between 100,000 and 1,000,000 transistors.
- ULSI – Ultra Large Scale Integration – It is a type of IC that has millions or billions of transistors on each chip. Such as the processor in a computer.
Diagram of IC
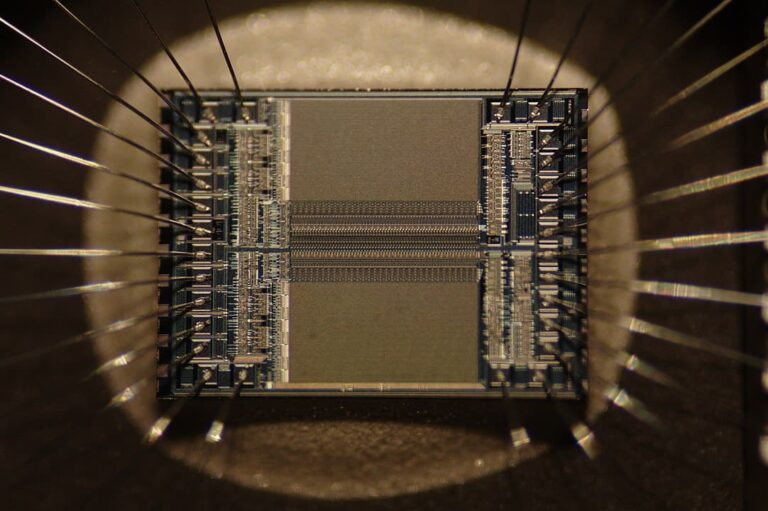
Advantages of IC
- The size of an IC as a whole is much smaller than that of a discrete circuit.
- When compared to whole discrete circuits, the weight of an IC is very small.
- It’s more likely to work.
- Because they are smaller, they use less electricity.
- In case it breaks, it is easy to replace but hard to fix.
- It has a faster-operating speed because it doesn’t have any parasitic or capacitance effects.
- There aren’t big differences in temperature between the parts of a circuit.
- It’s good for working with small signals.
- Because ICs are so small, they use less power, which is a good thing.
Disadvantages of IC
- You can’t make coils or indicators.
- It is not possible to do high-quality P-N-P assembly.
- It is hard to get a temperature coefficient that is low.
- The power that can be lost is capped at 10 watts.
- It’s not easy to get low noise and high voltage operation.
- You can’t make an inductor by hand.
How IC Works?
- An amplifier, timer, microprocessor, oscillator, and computer memory all work in the same way as an integrated circuit.
- Silicon is used to make an IC, which is a small wafer with thousands of parts like resistors, transistors, capacitors, and so on.
- These are small parts that can use analogue or digital technology to do different kinds of calculations to store data.
FAQ ( Frequently Asked Questions )
1. What is meant IC?
Ans – Integrated circuit (IC), also called a microelectronic circuit, microchip, or chip, is a group of electronic parts made as a single unit.
2. What is an IC and its function?
Ans – An IC can work as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, counter, logic gate, computer memory, microcontroller, or microprocessor. All modern electronics are made up of ICs, which are the basic building blocks.
3. What is IC in mobile?
Ans – IC stands for “integrated circuit,” and it is a very important microchip that can be found in the power section of every cell phone.
4. Which IC is used in smartphones?
Ans – BGA IC – Ball Grid Array
5. Who invented the silicon chip?
Ans – Jack Kilby , Robert Noyce , Frank Wanlass , Forrest S. Mozer
Image Source : Google

